如何写一个 kprobe 模块¶
问题¶
使用 bpftrace 之类的工具可以通过写脚本的方式很方便的 trace 内核函数,打印函数的参数、变量,但是涉及内核中一些比较复杂的数据结构,比如链表,而 bpf 没有提供对应结构的打印函数,自己处理起这些结构又比较麻烦的时候,可以考虑写一个 kprobe 模块,因为是内核模块,可以直接调用内核中的一切函数,比上层的高级工具更自由。
下面我们用一个实际的例子来看下如何来写一个 kprobe 模块。
内核中打开文件的时候有一个路径查找的过程,比如 /i9/b2/c3/exam,当调用 open 系统调用打开这个文件的时候,内核会按照 / 、 b2 、 c3 、 exam 这样的顺序一层一层的检查路径存在、权限啊之类的,内核不可能每次都从磁盘去读取这些数据,会将这些数据缓存在一个哈希表中。
这个路径查找的函数叫 __d_lookup ,每一层路径叫一个 dentry ,缓存哈希表叫 dentry_hashtable ,哈希的键是 (指向父 dentry 的指针, dentry 名) ,哈希表解决冲突使用的是链地址法。我们要写的模块,需要挂载到 __d_lookup 函数,打印出每一层路径哈希到表中之后对应的冲突链的长度(遇到的问题是有时候 open 文件时间太长,怀疑和这个冲突链太长有关系,类似 如何识别并解决复杂的dcache问题 这里的问题)。
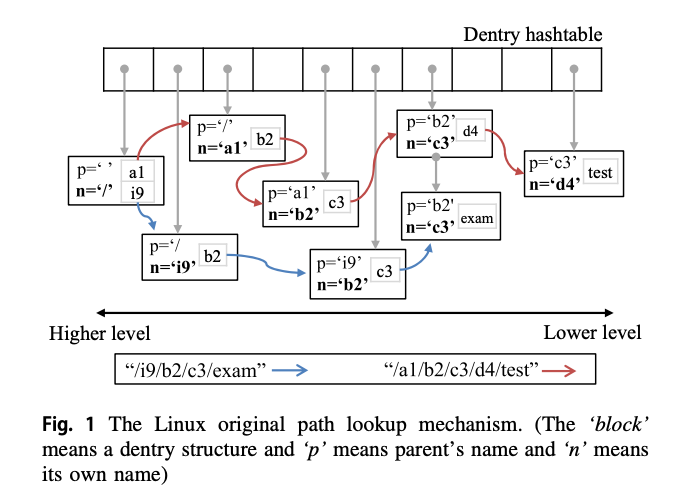
下面是 __d_lookup 函数中哈希某一层路径到表中并在对应的冲突链中查找这个路径的过程,我们需要做的就是挂载到这个函数上,用类似的逻辑遍历一个冲突链并打印出其长度。
struct dentry *__d_lookup(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
unsigned int hash = name->hash;
struct hlist_bl_head *b = d_hash(hash);
struct hlist_bl_node *node;
struct dentry *dentry;
...
rcu_read_lock();
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(dentry, node, b, d_hash) {
...
}
}
kprobe 模块的基本框架¶
代码:
// hlist_count.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kprobes.h>
static int __kprobes handler(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
printk("hello world!\n")
return 0;
}
struct kprobe kp = {
// 观察 `__d_lookup` 函数
.symbol_name = "__d_lookup",
// 在调用 `__d_lookup` 函数之前调用 handler 这个函数
.pre_handler = handler,
};
static int __init kprobe_init(void)
{
int ret = register_kprobe(&kp);
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("register_kprobe failed, returned %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
pr_info("planted kprobe at %p\n", kp.addr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit kprobe_exit(void)
{
unregister_kprobe(&kp);
pr_info("kprobe at %p unregistered\n", kp.addr);
}
module_init(kprobe_init)
module_exit(kprobe_exit)
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile:
obj-m := hlist_count.o
KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) clean
编译、加载、查看输出。
# make
# insmod hlist_count.ko
# dmesg
...
[15075.829231] Planted kprobe at ffffffff81278d60
[15075.832613] hello world!
查看生效中的 kprobe:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/kprobes/list
ffffffff816aab90 r tcp_finish_connect+0x0 [FTRACE]
ffffffff81278d60 k __d_lookup+0x0 [FTRACE]
如何调用/引用内核私有的函数或变量¶
dentry_hashtable 是个私有变量,没法直接引用,需要使用 kallsyms_lookup_name 来查找, kallsyms_lookup_name 函数可以返回 /proc/kallsyms 里面列出的所有符号的地址。
另外,哈希表的哈希函数是一个私有內联函数,需要把代码复制到自己代码里来使用,哈希函数里引用了另外一个私有变量,一并获取。
#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
static struct hlist_bl_head *dentry_hashtable;
static unsigned int d_hash_shift;
void *addr;
// 返回的是 dentry_hashtable 这个指针变量的地址,也就是 &dentry_hashtable
addr = kallsyms_lookup_name("dentry_hashtable");
if (!addr) {
return -EINVAL;
}
// 解引用
dentry_hashtable = *(struct hlist_bl_head **)addr;
// 获取哈希函数中引用的私有变量
addr = kallsyms_lookup_name("d_hash_shift");
if (!addr) {
return -EINVAL;
}
d_hash_shift = *(unsigned int*)addr;
如何获取函数的参数¶
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86_calling_conventions#System_V_AMD64_ABI
在 x86_64 架构下,前面 6 个函数的参数通过寄存器传递,分别为 %rdi , %rsi, %rdx , %rcx , %r8, %r9 。
对应到代码就是:
static int handler_pre(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs) {
...
regs->di, regs->si, regs->dx, regs->cx, regs->r8, regs->r9;
...
}
其余参数通过栈来传递。
计算和打印函数¶
把上面这些组合起来,实现上面框架中未实现的 handler 函数,就可以完成我们计算并打印哈希表冲突链长度的核心逻辑啦。
static struct hlist_bl_head *dentry_hashtable;
static unsigned int d_hash_shift;
// linux-4.14.69,不同版本的 d_hash 可能会不一样
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.14.69/source/fs/dcache.c#L112
static inline struct hlist_bl_head *d_hash(unsigned int hash)
{
return dentry_hashtable + (hash >> (32 - d_hash_shift));
}
static inline long hlist_count(const struct dentry *parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
long count = 0;
// 和 __d_lookup 函数中对应的查询循环逻辑类似
// https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.14.69/source/fs/dcache.c#L2281
unsigned int hash = name->hash;
struct hlist_bl_head *b = d_hash(hash);
struct hlist_bl_node *node;
struct dentry *dentry;
rcu_read_lock();
hlist_bl_for_each_entry_rcu(dentry, node, b, d_hash) {
count++;
}
rcu_read_unlock();
if (count > 2) {
printk("hlist_bl_head=%p, count=%ld, name=%s, hash=%u\n",b, count, name->name, name->hash);
}
return count;
}
static int __kprobes handler(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
int count = hlist_count(regs->di, regs->si);
return 0;
}
完整代码: https://github.com/chanfung032/labs/blob/master/hlist-count/hlist_count.c
